Types of Dashboards
There are three types of business dashboards which differ by area of use and the time employees spend on them.
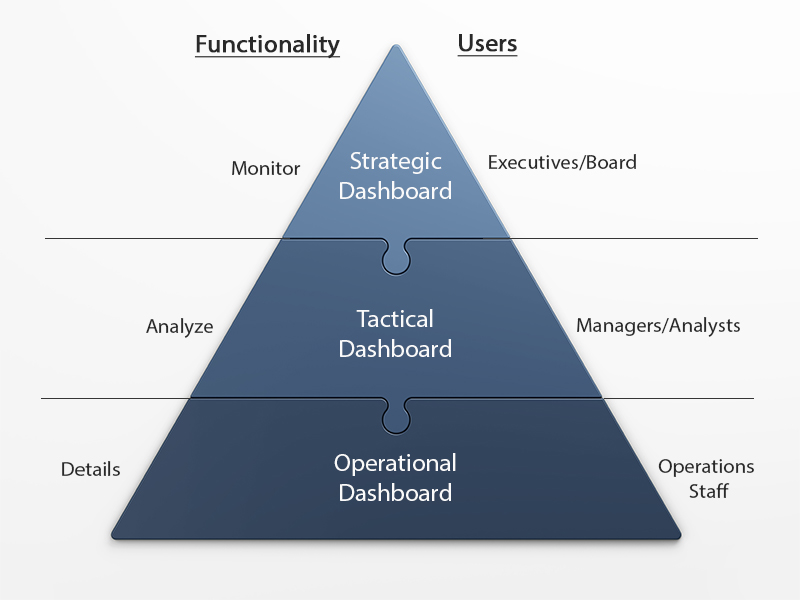
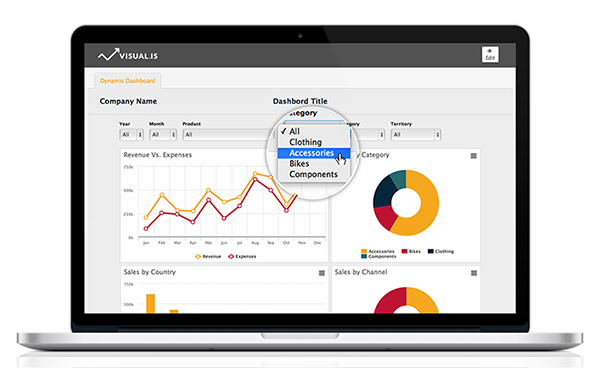
1) Strategic Dashboards
Used at the highest level of company management, strategic dashboards are designed with the balanced scorecard methodology in mind. Developed by David Norton and Robert Kaplan, this analysis technique is designed to create specific, quantifiable goals from an organization’s mission statement and business strategy. The method then allows its users to monitor performance in terms of achieving the company’s goals.
Strategic dashboards are used to monitor a company’s progress in achieving its predefined goals through relevant KPIs. For instance, for the sales department, dashboards record and track sales results, their trends and changes. Meanwhile, in the manufacturing department, production metrics are very important. Therefore, details such as product return date can identify positive and negative trends that can affect the company.
Business dashboards in this category also allow top level executives to see generalities first before delving into more detailed reports. To simplify the information and make it clear and transparent, increased data aggregation and graphic design are used.
2) Tactical Dashboards
Traditionally used by the middle management tier, tactical dashboards allow their users to assess the market’s reaction to their companies’ actions. However, some managers use this software internally, investigating how small changes or tasks influence their company as a whole. Regardless, users will get deeper insights into analyzed data and even solve problems by tracing their history and causes. Therefore, they can make better decisions which can improve a company’s stance in the present.
Unlike strategic dashboards, tactical ones are designed for more detailed purposes such as tracking trends related to the company’s goals and initiatives. For instance, a sales department using tactical dashboards won’t only see the totals, but also information regarding a product’s sale. Based on the information, sales managers can make decisions such as deciding to launch a product on a given date. On the other hand, quality is an important metric for the manufacturing department. Through their dashboard, supervisors can set regular quality review meetings among other related tasks.
3) Operational Dashboards
While the first two types of dashboards have a lot in common, operational dashboards significantly stand out. As their name suggests, they are used on an operational level in a given department, by its employees. As a result, they offer detailed insights, allowing their users to design work processes that increase benefits or revert trends. For instance, an operational dashboard in the sales department will allow employees to compare current sales with those from the month before. The software can also group sales data, identifying top salespeople and the best customers. As for the manufacturing department, comparing actual monthly production with target rates helps in identifying issues or opportunities.
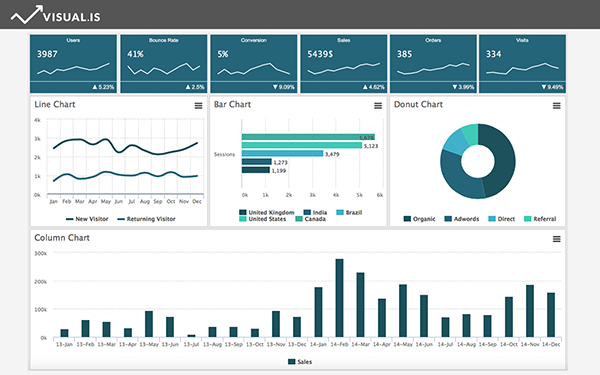
 Strategy– Once a company establishes strategies and tactics, managers can visualize and track their tactics with the help of strategy maps and scorecards. Modern, well-designed dashboards can be helpful in this regard, especially if they were effectively designed to display key performance-related charts and indicators as well. With time, these tools will help organizations focus on the most important performance-related activities and the factors which drive them.
Strategy– Once a company establishes strategies and tactics, managers can visualize and track their tactics with the help of strategy maps and scorecards. Modern, well-designed dashboards can be helpful in this regard, especially if they were effectively designed to display key performance-related charts and indicators as well. With time, these tools will help organizations focus on the most important performance-related activities and the factors which drive them. Planning– The main purpose of a dashboard is to enable managers to monitor, analyze and annotate. As a result, this software is linked strongly to planning and budgeting. For instance, executives can view, analyze and compare historical figures with forecasts, current budgets and targets. Similarly, they can monitor and share strategies and resource allocation figures across business units.
Planning– The main purpose of a dashboard is to enable managers to monitor, analyze and annotate. As a result, this software is linked strongly to planning and budgeting. For instance, executives can view, analyze and compare historical figures with forecasts, current budgets and targets. Similarly, they can monitor and share strategies and resource allocation figures across business units. Reporting– Because the software is designed for quicker decision making, displaying detailed reports may not be a common feature of dashboards. However, embedded links to reports can be part of a dashboard, offering more information for those who need more than charts and scorecards.
Reporting– Because the software is designed for quicker decision making, displaying detailed reports may not be a common feature of dashboards. However, embedded links to reports can be part of a dashboard, offering more information for those who need more than charts and scorecards. Analytics– Most modern dashboards offer users important analytical features, such as heat maps, statistical analysis and data mining. As a result, they enable executives or managers to answer pressing questions from the dashboard interface without logging in to other software or analytical modules.
Analytics– Most modern dashboards offer users important analytical features, such as heat maps, statistical analysis and data mining. As a result, they enable executives or managers to answer pressing questions from the dashboard interface without logging in to other software or analytical modules.